About Retina Eye Surgery
Common Retinal Problems
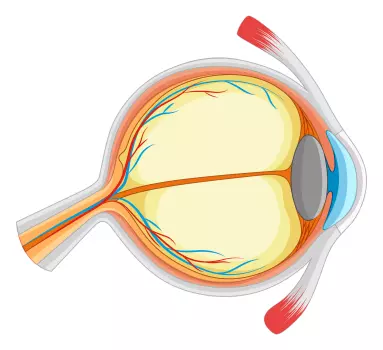
Retina's Structural Complexity
Function of the Retina
Light enters the eye and passes through the lens; it falls upon the retina. Inside the retina, specialised photoreceptor cells react to light by converting it into electrical signals. These signals travel through the optic nerve to the brain, where they are processed into the images we perceive.
Signs & Symptoms
Blurry or distorted vision.
Loss of peripheral vision.
Double vision or diplopia.
Light sensitivity.